Blog
Changing Landscape Between Dairy and Dairy Alternative Beverages

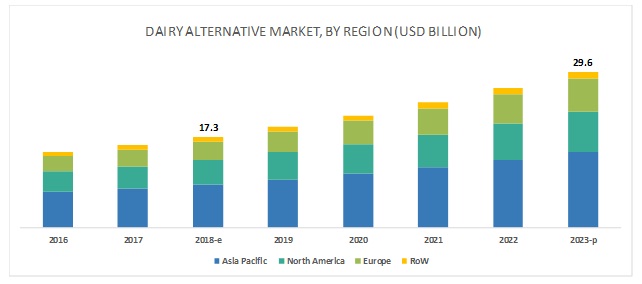
Within the past decade, plant-based dairy alternatives have increased in worldwide demand. The ‘Global Plant-based Beverages Market’ report valued the plant-based beverage industry at USD 11.16 billion in 2018. Additionally, it estimates the demand to surpass USD 19.67 billion by the end of 2023. The market is also likely to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of over 11% through 2028.
The combined rapid growth and profitability of plant-based dairy alternatives have gained the attention of those in the food industry. As a result, dairy manufacturers are incorporating plant-based alternatives into their production.
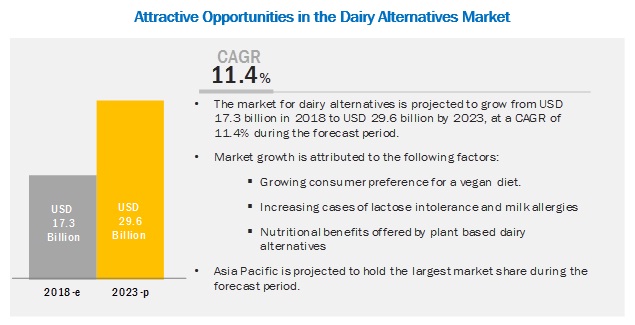
Attractive Opportunities in the Dairy Alternatives Market
Consumer Trends Inclined Toward Replacing Dairy with Plant-Based Alternatives
Over the same timeframe, dairy milk consumption continues to decline with each generation drinking fewer milk beverages than its predecessor. In Britain, for example, 25% of consumers are choosing plant-based beverages over traditional dairy beverages – with figures being as high as 33% for the young adult market (16 to 24-year-olds).

Increased awareness of lactose intolerance and dairy allergies is also driving interest to the plant-based beverage market. Ethnic origins impact the frequency of lactose intolerance: in South America, Africa, and Asia, over 50% of the population is intolerant. In some Asian countries, 100% of the population is intolerant. Yet in Northern Europeans, the intolerance range is between 5-17%. With the highest global rate of lactose intolerance, the Asian market also accounts for the largest share of the plant-based beverage market to date.
Plant-Based Alternatives
Awareness among consumers about the benefits of a vegan diet is another factor propelling the demand for plant-based dairy alternatives across the world. Several economies have seen a substantial increase in the vegan population. These consumers prefer dairy alternatives like soy, almond, rice, and other plant-based dairy alternatives as a substitute for dairy milk.
Because there is no stated definition, the Journal of Food Science and Technology attempted a general classification of the plant-based dairy alternatives. The five categories are:
- Cereal based:Oat, Rice, Corn, Spelt
- Legume based:Soy, Peanut, Lupin Cowpea
- Nut based:Almond, Coconut, Hazelnut, Pistachio, Walnut
- Seed based:Sesame, Flax, Hemp, Sunflower
- Pseudo-cereal based:Quinoa, Teff, Amaranth
Soy is the most consumed plant-based alternative in the world, dominating more than half of the total market share in 2018, and growing at CAGR of around 14%. The North American market demand for almond beverages was higher than soy milk for the first time.
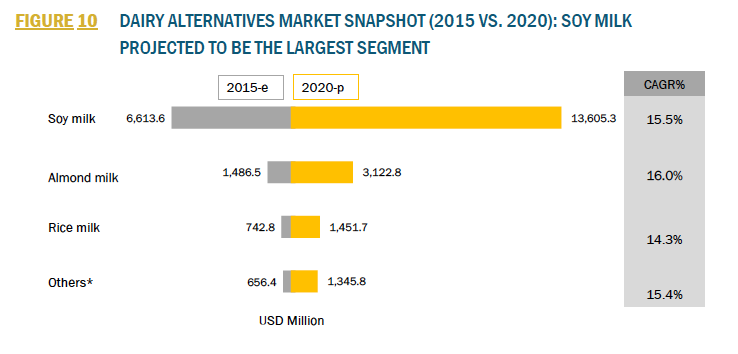
Oat beverages are growing in popularity due to their neutral taste and naturally creamy texture, which helps increase the demand when pairing with caffeinated beverages as well as on its own. Oat-based drinks fit a unique position of providing functionality more like dairy beverages while also appealing to consumers interested in sustainably sourced products.
Plant-Based Alternative Beverage Market – Overview
Companies moving into this emerging beverage market are finding success using innovative product launches and strategic partnerships to increase their presence. These innovative product formulations also helping to increase the market size and grow demand for more plant-based beverages.
In April 2017, the Groupe Danone (France) acquired The WhiteWave Foods Company: a company focused on producing plant-based foods, beverages, and coffees. Manufacturers like Groupe Danone, who are already operating in the plant-based dairy alternative market, are also focusing on expanding the appeal of their products by tapping into innovative replacements and approaches. The plant-based and caffeinated beverage producing companies are vying to discover what consumers want to purchase, which will enable them to incorporate the same in their products via new additions.
The Italian Dairy Granarolo (Italy) launched a range of plant-based beverages to grow its market share in the beverage market.
In 2018, Nestle S.A. (Switzerland) launched in Mexico with an almond/fruit juice beverage under the brand Nature’s Healthy Brand.
The USA based Dairy Farmers of America launched lactose-free milk blended with plant-based almond
New Processing Challenges with Plant-Based Beverages
Dairies that are expanding into the low-acid, plant-based beverage market must update risk assessments and manufacturing procedures to incorporate new physical, chemical, and biological risks as well as technological barriers. Working with raw commodities brings an increased risk of chemical residues like pesticides and mycotoxins that differ in prevalence and type compared to raw milk. Manufacturing a broader range of beverages that contain allergenic ingredients significantly increases the risk of allergen cross-contamination and associated recalls from mislabeling.

The physiological composition of plant-based dairy alternatives also brings processing challenges as the composition and structure of raw milk are significantly different from plants. Consumers are expecting plant-based dairy alternatives to have similar physiochemical and sensory attributes. From creaminess, mouthfeel, and color, to how these plant-based beverages react when being used in cold and hot temperatures, they want their plant-based beverages to feel and taste like milk.
Therefore, dairy processors are working to create ways to create not only a similar nutritional specification but also the stability and homogeneity of the product. They are blending plant oils, water, emulsifiers, and other additives. Once combined, manufacturers thermally process all the ingredients to produce a stable product with the desired attributes.
Many of the plant-based crops and ingredient flavors utilized, like cocoa powder, are commodities grown in warm temperatures with high humidity that are ideal conditions for the growth of mold and mycotoxins.
Cocoa Powder |
|||||
|
Country |
Mycotoxin tested |
Number of Positive Samples |
Mean Concentration (ppb) |
Maximum Concentration (ppb) |
Analysis Method |
| Italy | Ochratoxin | 40/40 | 0.5 | 1.82 | HPLC |
| Brazil | Ochratoxin | 25/25 | 0.39 | 0.92 | HPLC/FLD |
| Canada | Ochratoxin | N=15 | 1.2 | 4.7 | HPLC/FLD |
| Brazil | Aflatoxin | 24/25 | 0.53 | 1.7 | HPLC/FLD |
| Canada | Aflatoxin | N=15 | 1.2 | 3.52 | HPLC/FLD |
- Beverages 2018, 4(4), 83: https://doi.org/3390/beverages4040083
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs
In processing soybeans, ochratoxin is detectable at all steps of soy milk processing; from the raw soybean, all the way to the finished product. Although ochratoxin levels decrease in the finished product, this still illustrates the need for expanded verification programs testing raw materials before receiving them at the plant.

Differences in environmental conditions of raw materials lead to diverse microorganisms entering the processing plant. This diversity increases the risk of biological contamination and requires a broader understanding of the effects of pH, water activity, and upstream processing of raw ingredients compared to traditional dairy.
The Greater the Risk, the Greater the Reward
Although the plant-based beverages are more challenging to develop, consistently produce, and have more risk factors for the dairy processing operation, they offer higher profitability and an increase in market share compared to traditional dairy.
About Charm Sciences
Established in 1978 in Greater Boston, Charm Sciences helps protect consumers, manufacturers, and global brands from a variety of issues through the development of food safety, water quality, and environmental diagnostics tests and equipment. Selling directly and through its network of distributors, Charm’s products serve the dairy, feed and grain, food and beverage, water, healthcare, environmental, and industrial markets in more than 100 countries around the globe.

